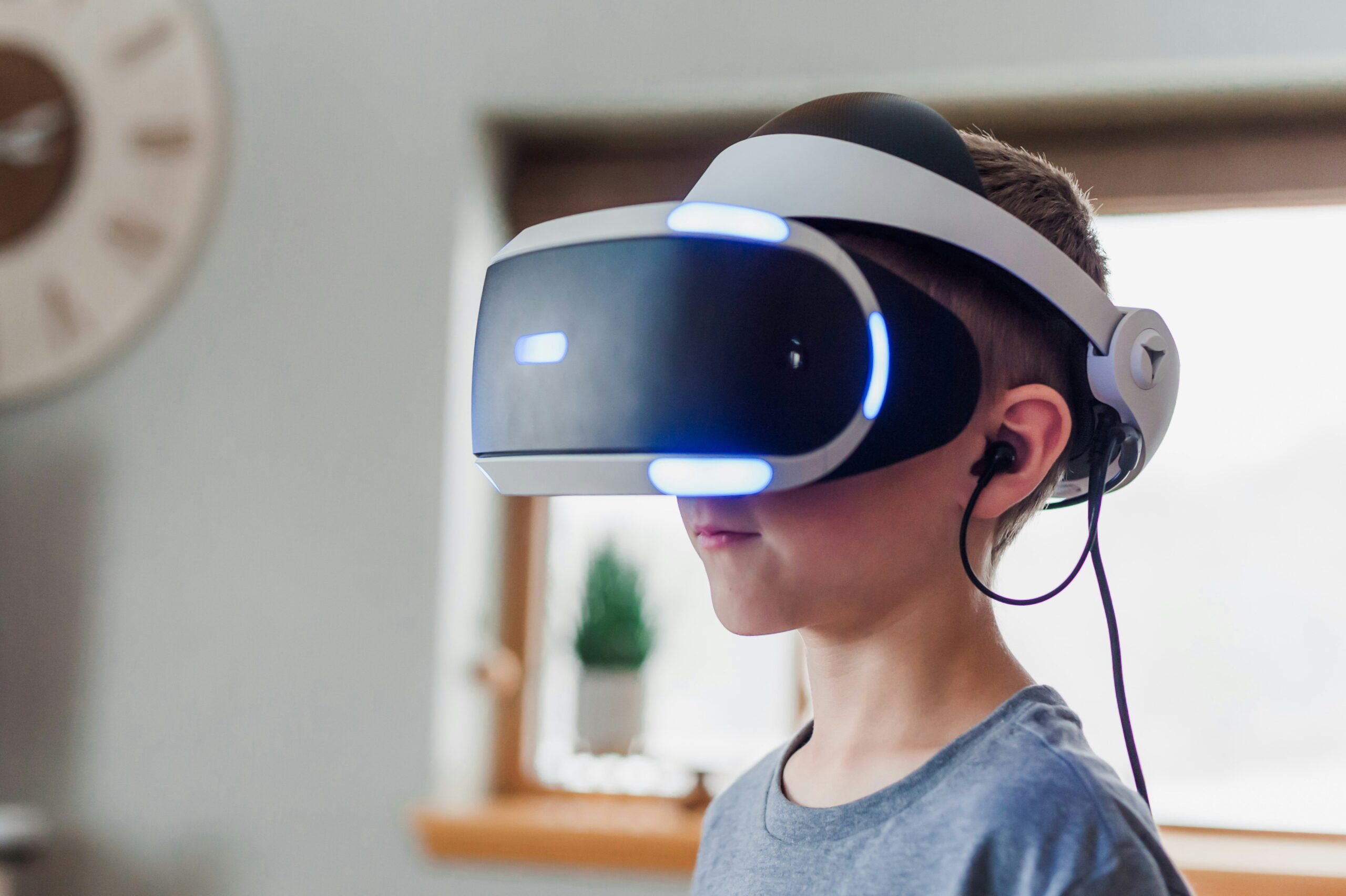
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), collectively known as extended reality (XR), have gained significant popularity in recent years. As these technologies continue to evolve, it is crucial to understand the importance of user experience (UX) design. One of the key aspects of XR UX design is considering human factors, which play a vital role in creating immersive and user-friendly experiences.
Understanding Human Factors
Human factors refer to the physical, cognitive, and social attributes of individuals that influence their interactions with technology. In the context of XR, understanding human factors is essential for designing interfaces that are comfortable, intuitive, and engaging.
Ergonomics
Ergonomics focuses on designing XR experiences that are physically comfortable and minimize fatigue or discomfort. This includes considerations such as the weight and fit of the headset, the placement of controls and buttons, and the overall design of the user interface. By prioritizing ergonomics, designers can ensure that users can comfortably engage with XR content for extended periods without experiencing discomfort.
Cognitive Load
Cognitive load refers to the mental effort required to understand and interact with XR content. Designers must carefully consider the complexity of the interface, the clarity of instructions, and the ease of navigation. Minimizing cognitive load allows users to focus on the content and experience rather than struggling with the interface. This can be achieved through clear visual cues, intuitive interactions, and well-structured information architecture.
Sensory Experience
In XR, the sensory experience plays a significant role in creating a sense of immersion. Designers need to consider how visual, auditory, and tactile cues can enhance the overall experience. This includes factors such as the quality of graphics, the accuracy of sound spatialization, and the responsiveness of haptic feedback. By carefully crafting the sensory experience, designers can create a more realistic and engaging XR environment.
Designing for Accessibility
Accessibility is a critical aspect of XR UX design. Designers must ensure that XR experiences are inclusive and can be enjoyed by users with diverse abilities. Considerations for accessibility include:
Physical Accessibility
Designing XR experiences that can be accessed and enjoyed by individuals with physical disabilities is essential. This may involve providing alternative input methods, such as voice commands or gesture recognition, to accommodate users who may have limited mobility. Additionally, designers should consider the physical space required for XR experiences, ensuring that users can comfortably move around and interact with the virtual environment.
Visual Accessibility
Visual accessibility involves designing XR experiences that are accessible to individuals with visual impairments. This may include providing alternative text descriptions for visual elements, utilizing high contrast colors, and ensuring that important information is conveyed through multiple modalities, such as audio or haptic feedback.
Cognitive Accessibility
Cognitive accessibility focuses on designing XR experiences that are easily understandable and navigable for individuals with cognitive impairments. This may involve simplifying instructions, providing clear visual cues, and minimizing distractions within the virtual environment.
User Testing and Iteration
When designing XR experiences, user testing is crucial to ensure that the interface and overall experience meet the needs of the target audience. By conducting user tests, designers can gather valuable feedback and identify areas for improvement. This iterative design process allows for continuous refinement and optimization of the XR UX, resulting in a more user-friendly and engaging experience.
Conclusion
Considering human factors is essential for creating immersive and user-friendly XR experiences. By prioritizing ergonomics, minimizing cognitive load, and designing for accessibility, designers can create interfaces that are comfortable, intuitive, and inclusive. User testing and iteration further enhance the XR UX, ensuring that the final product meets the needs and expectations of the users. As XR continues to evolve, understanding and incorporating human factors will be key to creating compelling and successful XR experiences.






Leave a Reply